In corporate networks, various mechanisms are often used to control access to organizational resources. These mechanisms are based on the 802.1x protocol, which provides network security through authentication. As a result of authorization users or devices can access specific subnets. One of the safer ways, that can be used for this purpose- is the EAP-TLS method,using PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) and certificates.
Appropriate access certificates for users are generated in the PKI server, and also, must be installed on the end device. It is important to verify the correctness of the server's certificate. The client’s certificate is to be verified (must be signed by a known Certification Authority) before the username is checked against the authentication server.
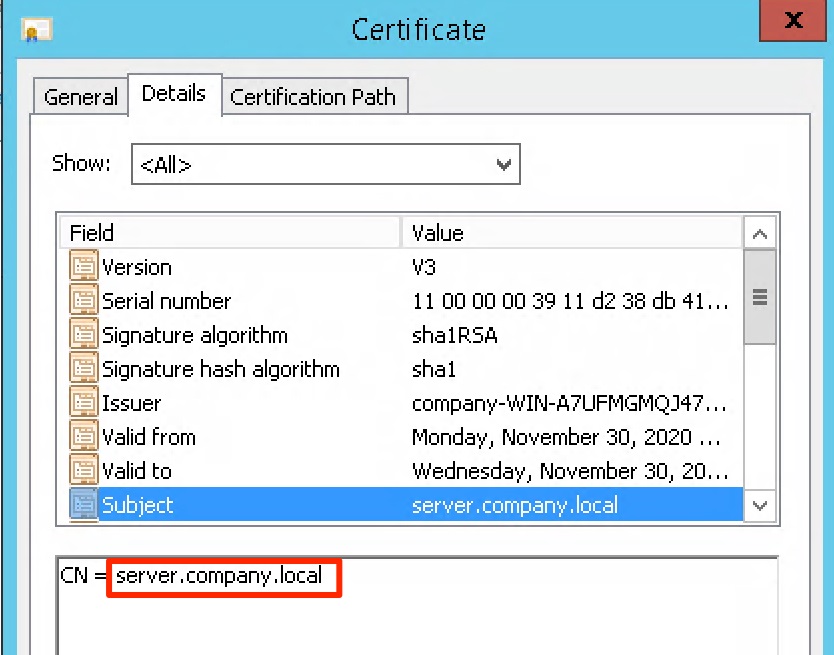
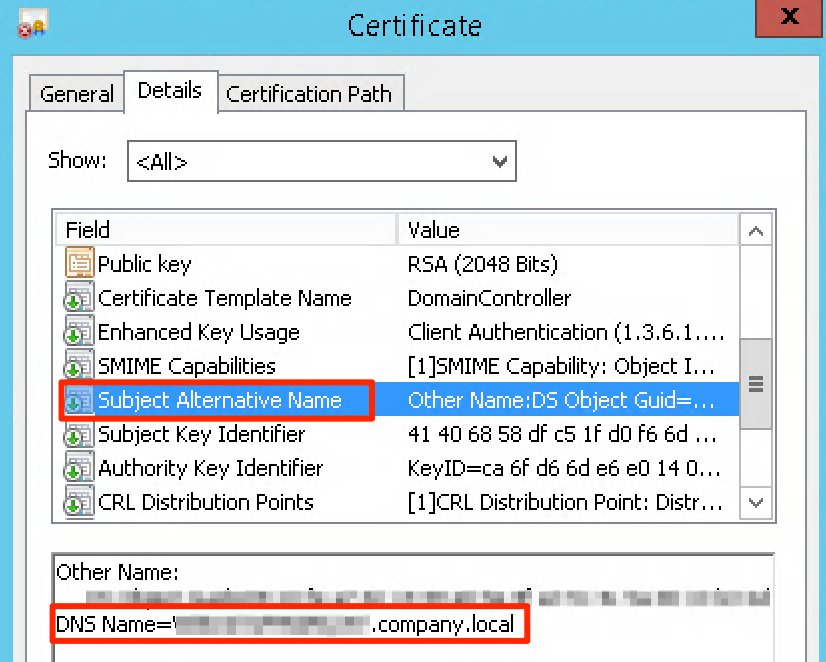
With the release of the new Windows 11 operating system, the way how to verify server certificates has changed. A more restrictive policy of validating the server name compatibility with the information, contained in the certificate, has been imposed. On Windows 10 systems, the value from the Subject field is used for comparison, whereas on Windows 11, this value is in the Subject Alternative Names field.
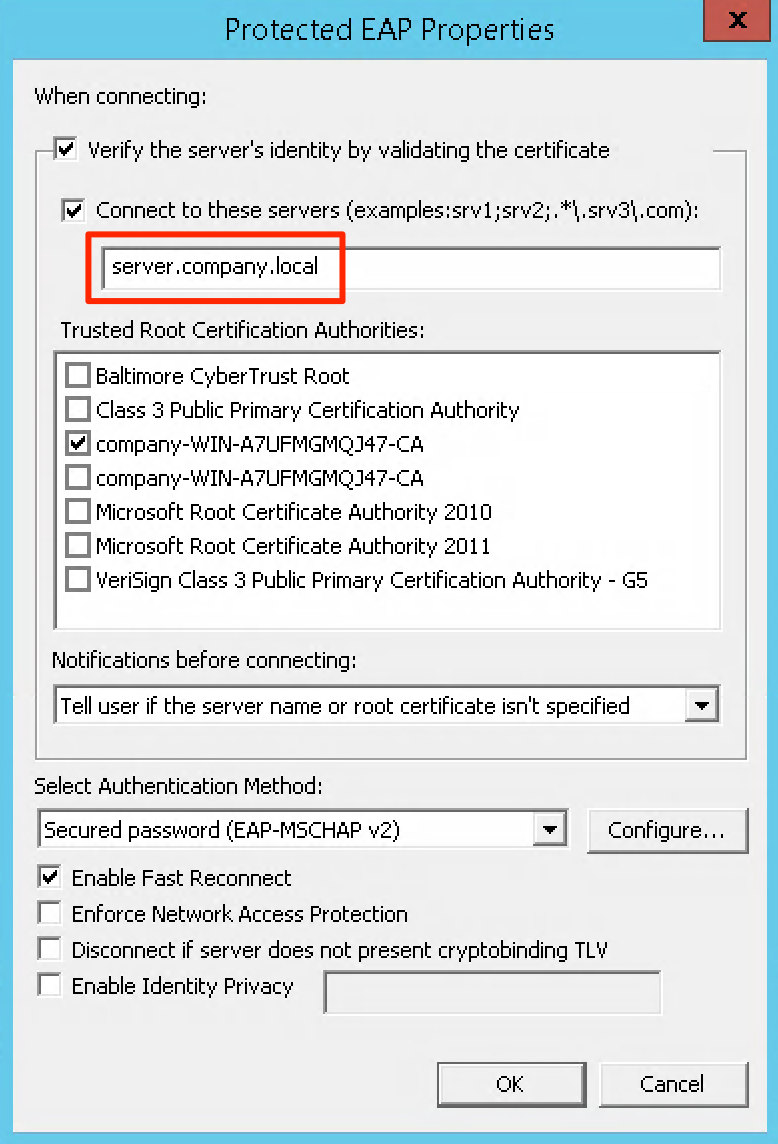
When generating the server certificate we recommend that you configure the name settings in the Subject field and the Subject Alternative Names field. This will allow you to create a universal verification mechanism for both Windows 11 and Windows 10 systems working correctly. In some networks it may also be a good idea to add additional IP addresses as alternative server names. On the supplicant’s side, it is also possible to use the appropriate option to select a previously installed certificate and choose the server name verification option by entering the required name in accordance with the format in the system prompt.